


| Pair Name | Curcumin, Binimetinib | ||
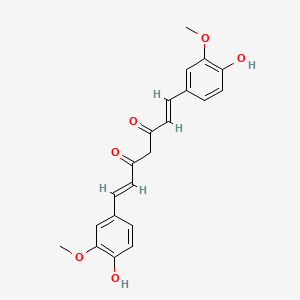
| Phytochemical Name | Curcumin (PubChem CID: 969516 ) | ||
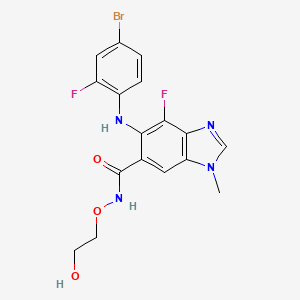
| Anticancer drug Name | Binimetinib (PubChem CID: 10288191 ) | ||
| Structure of Phytochemical |
|
Download
2D
MOL
3D
MOL
|
|
| Structure of Anticancer Drug |
|
Download
2D
MOL
3D
MOL
|
|
| Pair Name | Curcumin, Binimetinib | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C30] | Melanoma | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Necroptosis | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | MCL1 | hsa4170 |
| Down-regulation | Expression | BCL2 | hsa596 | |
| Up-regulation | Cleavage | CASP3 | hsa836 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | TP53 | hsa7157 | |
| Up-regulation | Phosphorylation | RIPK3 | hsa11035 | |
| Up-regulation | Phosphorylation | MLKL | hsa197259 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | BAX | hsa581 | |
| In Vitro Model | G361 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_C8ZL |
| SK-MEL-2 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0069 | |
| Result | Our data demonstrates that curcumin exerts significant synergistic anticancer effects on MM cells by inducing ROS and necroptosis when combined with binimetinib. Therefore, a strategy of adding curcumin to conventional anticancer agents holds promise for treating MM. | |||
| No. | Title | Href |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Curcumin Enhances the Anticancer Effects of Binimetinib on Melanoma Cells by Inducing Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Cell Apoptosis with Necroptosis. Ann Dermatol. 2023 Jun;35(3):217-228. doi: 10.5021/ad.22.200. | Click |
